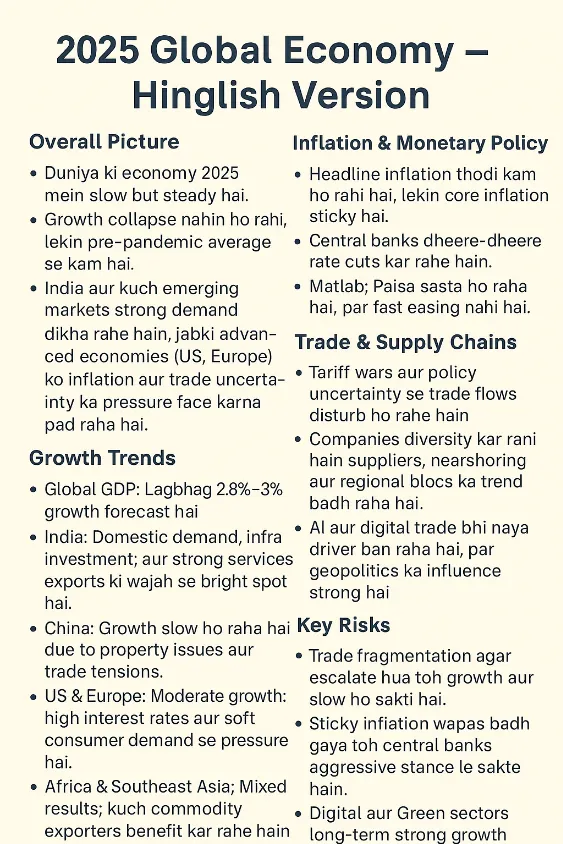
The world economy in 2025 is moving through a slow but resilient phase. Growth is not collapsing, but it is weaker than pre-pandemic averages. Some regions, especially large emerging markets like India, are showing strong momentum, while advanced economies such as the U.S. and Europe face pressures from sticky inflation, cautious monetary policy, and trade uncertainty.
Growth Economy Patterns
- Global GDP: Forecasts suggest growth around 2.8%–3% this year.
- India: Remains a global bright spot, supported by infrastructure investment, domestic consumption, and strong services exports.
- China: Slowing down due to property-sector challenges, demographic headwinds, and trade tensions.
- U.S. & Europe: Experiencing modest growth. High interest rates and softer consumer demand are weighing on momentum.
- Africa & Southeast Asia: Mixed results – some commodity exporters are benefiting, while others are struggling with debt burdens and inflation.

Economy Inflation & Monetary Policy
- Headline inflation is cooling, but core inflation (excluding food and energy) remains sticky.
- Central banks are easing cautiously:
- The U.S. Federal Reserve has begun rate cuts but at a gradual pace.
- European and Asian central banks are also calibrating carefully, balancing growth with inflation risks.
- This means borrowing costs are slowly coming down, but liquidity is not yet as loose as businesses hoped.

Trade & Supply Chains
- Global trade is under stress due to tariff escalations, reciprocal trade measures, and policy shifts.
- Many economies are pursuing “China +1” strategies, diversifying suppliers, reshoring, and building regional trade blocs.
- Technology and AI-driven trade flows are emerging, but geopolitics continues to heavily influence them.

Major Risks
- Trade fragmentation: Escalating tariffs could slow trade growth further.
- Sticky inflation: If prices rise again, central banks may halt or reverse easing.
- Debt stress: Several emerging economies face heavy external debt obligations.
- Geopolitical shocks: Energy disruptions, semiconductor supply limits, and regional conflicts could unsettle markets.
- Climate risks: Extreme weather events are impacting agriculture, infrastructure, and insurance costs.
- BMI Calculator
- Firozabad AQI:कांच की चमक के पीछे धुंधलाता
- 2026 Kia Seltos HTE ने ‘Base Model’ की परिभाषा बदल दी है?
- Global Hunger Index (2026): स्थिरता और संकट के बीच जूझती दुनिया
- Firozabad ka aqi kitna hai
Practical Implications
- Diversification is essential: Businesses should reduce reliance on a single market or supplier.
- Focus on demand-driven markets: Economies with strong domestic consumption (India, Indonesia, etc.) offer better growth opportunities.
- Invest in transformation sectors: AI, digitalization, renewable energy, and green infrastructure remain promising long-term bets.
- Policy predictability matters: Countries with stable and transparent policies will attract more investment.
👉 Bottom Line:
The global economy in 2025 is defined by cautious optimism. Growth is present but uneven, risks remain significant, and resilience depends on diversification, innovation, and smart policy choices.
- iPhone 17 Pro Max Launch Date: 10 Reasons to Wait for iPhone 17 Series
- Green Vegetables Benefits – हरी सब्ज़ी खाने से होने वाले 10 बड़े फायदे
- क्या BRICS देश मिलकर अपनी मुद्रा बना सकते है?
- QUAD की बैठक; India-America की तनातनी के बीच क्या रद्द होगी ?
- JPG to PNG to WEBP converter
- Convert Any File Into PDF
- Facts About Tomatoes That You May Not Know
- Age Calculator
- Rashii Khanna: Biography, Career, Movies, Awards and Unknown Facts
- Vicky Kaushal & Katrina Kaif Announce Pregnancy: A New Chapter Begins